线段树基础复习
条评论线段树
线段树主要用于维护区间问题,常见应用如区间加,区间乘,区间最值等,还有一些其他应用,如区间开平方,求解最大子段和,最大连续子段长度等等。
虽然写起来没有树状数组轻便,但是实现起来很多时候思维难度要小于树状数组,也能完成某些树状数组完成不了的工作。
一般的线段树都是$O(nlogn)$的,但是某些经过特殊处理的线段树能够在某个方面(询问,或者区间赋值等)达到更优秀的复杂度,如珂朵莉树和猫树。
一些题目
🆗HDU1394
题意
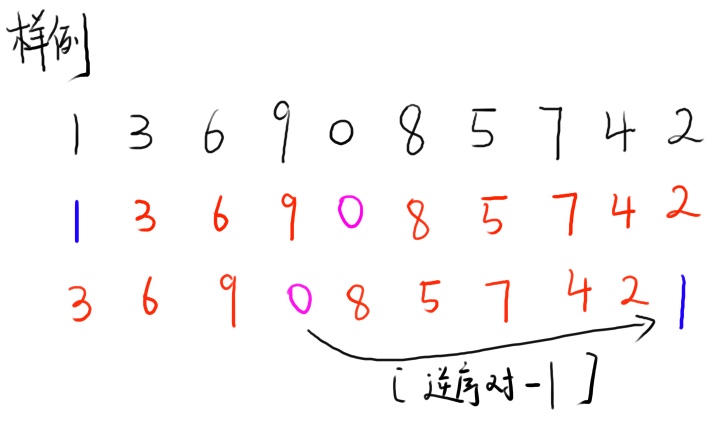
给出一个长度为$n$的初始数列,你可以循环该数列,找到所有数列中逆序对最小的一个,并输出这个数列逆序对的个数。
循环该数列时,下标变化形如如:$[1,2,\dots,n] \rightarrow [2,3,\dots,n,1] \rightarrow \dots$
考察
单点修改+区间询问,逆序对
分析
首先求出初始数列的逆序对个数。维护一颗权值线段树,一边读入一边插入元素,插入完成后询问比该元素大的元素有多少个(Update(1, a[i], a[i], 1, tree); Query(1, a[i] + 1, n, tree))。统计Query的和就为初始数列的逆序对个数。
然后,分析每次循环数列的贡献。
每次循环数列后,上一个数列最开始的元素会被转移到数列的末端。
也就是说,逆序对个数会减少【比被转移元素小的元素个数】,增加【比被转移元素大的元素个数】。
原因如图所示(红色数字个数为增加的逆序对个数,粉色为减少的逆序对个数):
代码没有需要特别注意的地方,就是基础的线段树板子。
Code
1 |
|
🆗HDU1698
题意
有一初始值均为$1$的数列,现在每次指定区间$[a, b]$,将区间内的值替换为$1 \ or \ 2 \ or \ 3$,求最后该数列的和。
考察
区间赋值+区间询问
分析
只需要把线段树区间求和的模板,+=的部分改为=,就可以$AC$。
Code
1 |
|
🆗LG4513
题意
给出一个数列,有两种操作:
①选择其中一个项修改为任意值;
②求区间$[a,b]$中最大的子段和。
考察
单点修改+最大子段和
分析
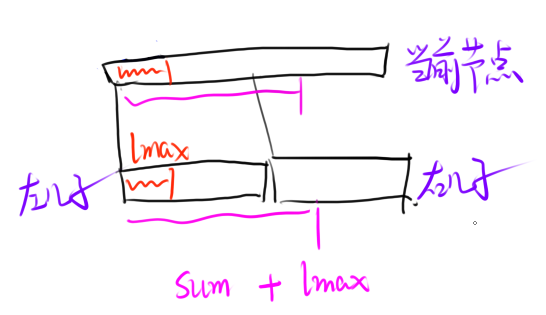
最大子段和可以归为三种情况:
- 该子段存在于目前线段树节点的左区间
- 该子段存在于目前线段树节点的右区间
- 该子段横跨了目前线段树节点的左右区间
要求最大子段和,可以考虑维护
- 从区间左端点能够选出的最大子段和(一定包含左端点)(简称为$lmax$)
- 从区间右端点能够选出的最大子段和(一定包含右端点)(简称为$rmax$)
- 该区间内的最大子段和(无限制)(简称为$mx$)
- 该区间内的元素和(简称为$sum$,若有左右儿子则分别为$lsum,rsum$)
其中:
先考虑边界情况:
在递归到目前节点只有一个元素时,有
$lmax=rmax=mx=sum当前元素$
然后考虑其他情况:
由于$lmax$一定要取到区间左端点,因此当前节点的$lmax$至少等于左儿子的$lmax$。
另外,若当前左儿子的$sum$加上右儿子的$lmax$更大的话,则更新$lmax$。
取左儿子的$sum$是保证一定包含左节点,取右儿子的$lmax$是保证连续性。
$rmax$同理转移。
那么$mx$呢?
取$max{lson’s\ mx,rson’s \ mx,lson’s \ rmax + rson’s \ lmax} $即可。
取$lson’s \ rmax + rson’s \ lmax$的原因与上面相同,都是为了保证连续性。
最后,在$Query$函数中,由于需要维护左右儿子节点的各种参数,因此将返回值设为$SegmentTree$,每次返回对应节点线段树所维护的信息即可。
如果访问到了不需要的区间,为了避免对最终答案造成贡献,返回一个$mx,lmax,rmax$均为极小值的节点即可。
Code
1 |
|
🆗HDU1540
题意
给出一个初始均为$1$的数列,每次有两个操作:
①选择一个元素变为$0$
②询问包含位置$pos$的由连续的$1$组成的段的最大长度
考察
单点修改+最长连续子段
分析
这一题和上面那题差不多。
难点在于这个段必须全部由$1$构成,这就要求修改$Update$和$Pushup$的过程来帮助解决这道题目。
首先,考虑边界情况,当节点只有一个元素时:
$lmax=rmax=val = 1$
然后,考虑节点有多个元素的情况:
由于$lmax$一定要包含区间的左节点,当前节点的$lmax$至少为左儿子的$lmax$。
这一点与上一题的一样的。
但是什么情况下才能像上一题一样有左儿子的$sum$加右儿子的$lmax$?
容易知道若左儿子都为连续的$1$,则有$rt - lf + 1 == lmax \ or \ rmax$。
也就是说只要左儿子节点满足这个条件就可以进行转移了。
右儿子同理。
另外一个难点在于对询问的处理。
这次询问的是包含某一特定点的连续子段。
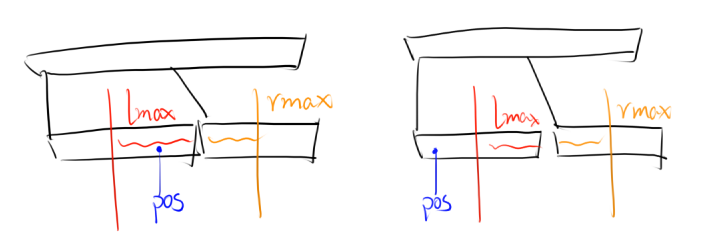
同样先考虑能够结束的边界情况:
①当节点满足$lf == rt$时:
此时若节点为$1$,则返回$1$,否则为$0$;
②当节点恰好处在左儿子的$rmax$范围内:
直接返回$rmax$+右儿子的$lmax$;
③当节点恰好处在右儿子的$lmax$范围内:
直接返回$lmax$+左儿子的$rmax$;
然后考虑不能结束的其他情况:
④只要不满足上面的三个条件,就为不能结束的其他情况。
这需要需要进一步递归求解。
虽然我们不能直接结束,但能够确定需要寻找的位置在左儿子还是在右儿子。
这便于进一步分解大问题为可以直接结束的小问题。
②③④情况如图所示:
大概思路如上,剩下的就是代码实现了。
需要注意这题是多组数据,题面没说…
Code
1 |
|
另解
考虑维护距离当前点的最近的被破坏的点。考虑维护两颗线段树,初始值均设为$0$。
然后,两颗线段树一颗维护最大值,一颗维护最小值。
每有村子被破坏时,将该点更新为对应的编号。
这样,设每次被破坏的点为$pos$,每次只需要在$[1, pos-1]$中寻找最大值,和在$[pos+1, n]$中寻找最小值,就是距离当前点最近的被破坏的点了。
结束
考前就写一下这些基本的先。
更多数据结构以后刷专题的时候再做一波。
啊,想起做线段树还不是因为上次ICPC复盘写炸了…